In an innovative leap toward environmental sustainability, a chemistry student from the University of Surrey, UK, has developed a robot fish named “Gillbert” that actively eats microplastics from rivers and lakes. The invention is part of a growing wave of biomimetic robotics, where machines are designed to mimic nature’s forms and functions.
Gillbert was created as an entry in the Natural Robotics Contest, a global competition that encourages eco-conscious design. The robot fish earned praise for its simple yet impactful functionality—removing harmful microplastics from water while swimming like a real fish.
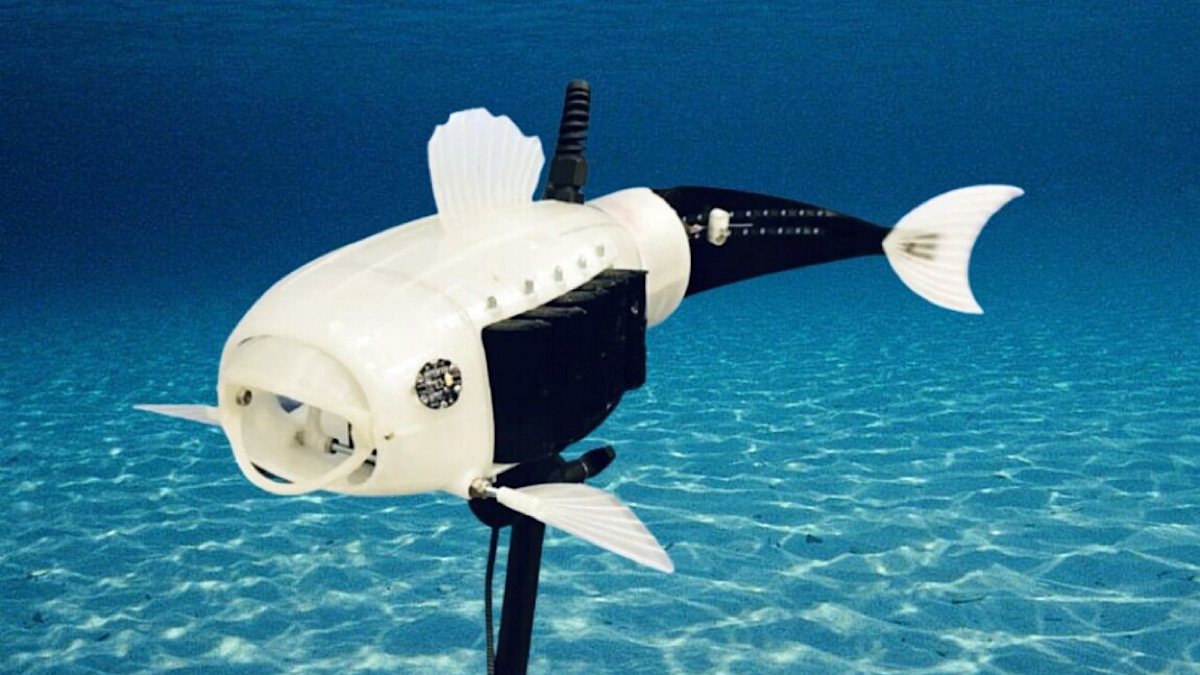
How Does Gillbert Work?
Gillbert is about 50 centimeters long, roughly the size of a salmon, and is equipped with a flexible tail for realistic swimming motion. As it moves through water, specialized gill-like filters on its sides suck in water, capturing microplastics using fine nylon mesh. These particles, often invisible to the naked eye, are stored in a small chamber inside the robot.
The current version is remotely controlled, but future models are expected to be autonomous and capable of swimming in natural water bodies independently.
Why Gillbert Matters
Microplastics—tiny plastic particles under 5mm in size—are polluting water bodies worldwide and entering the food chain through aquatic life. These particles are found in bottled water, seafood, and even table salt. Gillbert’s design presents a low-cost, effective, and sustainable method to tackle microplastic pollution at its source.
Moreover, the robot is made using 3D-printed parts and open-source designs, making it accessible for students, researchers, and environmentalists globally.
A New Age of Eco-Robots
Gillbert isn’t just a student project; it’s part of a larger movement in environmental robotics. The Natural Robotics Contest organizers highlighted it as a “perfect example” of how nature-inspired design can address real-world challenges. The aim is to encourage more engineers and creators to develop practical, affordable, and nature-friendly tech solutions for the planet.
As climate change and pollution continue to threaten ecosystems, such creative solutions offer hope — and action.
