Diabetes is more than just high blood sugar—it’s a serious health condition that can damage multiple organs if not controlled. When the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or fails to use it effectively, glucose levels rise, leading to long-term complications. Many people underestimate the dangers of consistently high blood sugar, but ignoring it can severely affect overall health.
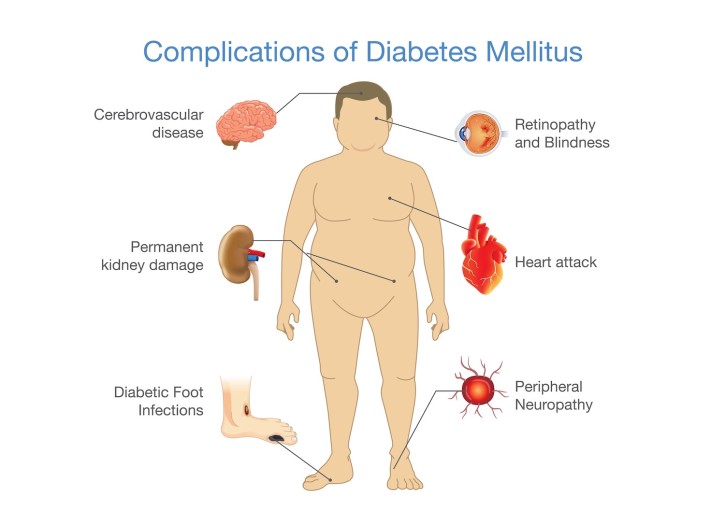
Here are some of the most common complications caused by uncontrolled diabetes:
Kidney Disease (Diabetic Nephropathy)
Excess glucose in the blood damages the small blood vessels in the kidneys, affecting their ability to filter waste. Over time, this can lead to protein leakage in urine, chronic kidney disease, and in severe cases, dialysis or kidney transplant may be required.
Nerve Damage (Diabetic Neuropathy)
Persistently high sugar levels can harm nerves, particularly in the legs and feet. This results in tingling, burning sensations, pain, or numbness. Because of reduced sensation, even minor injuries may go unnoticed, increasing the risk of severe infections.
Heart Disease and Stroke
High blood sugar accelerates the buildup of fatty deposits in the arteries, raising the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and hypertension. Diabetics are significantly more prone to cardiovascular diseases compared to non-diabetics.
Eye Problems (Diabetic Retinopathy)
Excess glucose damages the blood vessels in the retina, leading to blurred vision, cataracts, or in severe cases, blindness. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to protect eyesight.
Foot Complications
Poor circulation and nerve damage reduce the body’s ability to heal wounds. Small cuts or blisters may develop into serious infections, which, if untreated, can lead to ulcers or even amputations.
Skin and Gum Infections
Weakened immunity in diabetics makes them more susceptible to bacterial and fungal infections. This often results in slow-healing skin conditions and gum disease.
Cognitive Decline
Studies suggest that uncontrolled diabetes increases the risk of memory loss, dementia, and other cognitive impairments, especially in older adults.
